Feb . 08, 2025 06:42 Back to list
Vinvy White Dry Wall PVC Profile PVC Corner Bead Angle Bead for Building
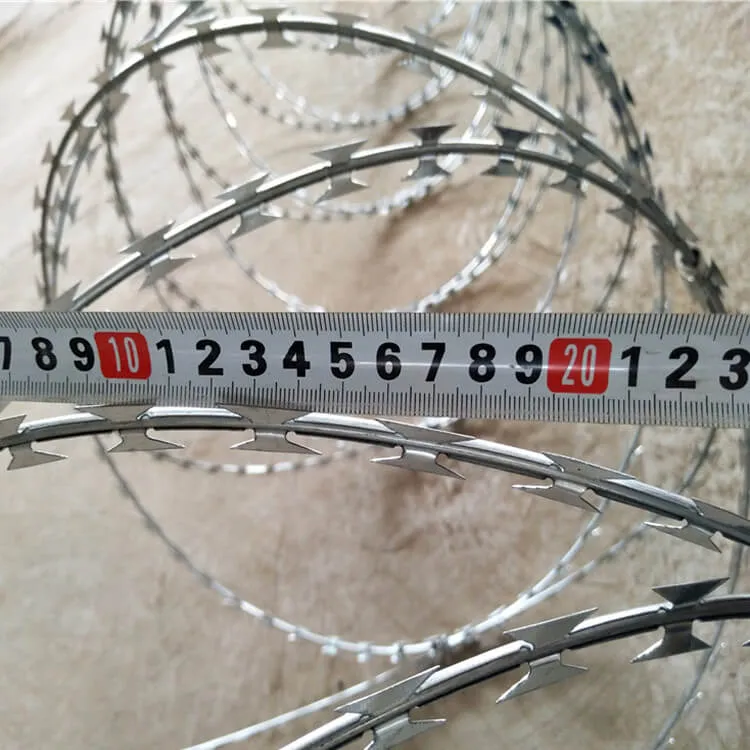


Field experience consistently reaffirms the importance of proper installation techniques when working with corner beams. Improperly installed beams can lead to catastrophic failures or necessitate costly repairs and retrofitting. As such, skilled craftsmanship and adherence to building codes and standards are non-negotiable facets of their installation process. This practical experience fosters trust between builders and clients, ensuring that projects conclude successfully and sustainably. Addressing the authoritative aspect, code compliance plays an integral role. International and local building codes prescribe specific standards for the materials and installation procedures for corner beams. Adhering to these codes not only guarantees safety but also enhances the credibility and reputation of construction professionals. Expertise in navigating these codes and offering solutions that meet or exceed them is a marker of authority in the field. Trustworthiness in utilizing corner beams is established through documented case studies and the transparent communication of past project successes and lessons learned. Architects and engineers often publish white papers and attend industry conferences, sharing their insights and pioneering methods. Such knowledge exchange bolsters the collective understanding and fosters the ongoing evolution of construction practices. In conclusion, the corner beam is a pivotal element within the architecture of any building, marrying the principles of structural engineering with the realities of modern construction needs. Through thoughtful material selection, rigorous engineering design, and meticulous installation, corner beams ensure that structures remain safe, durable, and aesthetically pleasing. As our built environments become increasingly complex, the demand for expertise and authoritative practices concerning corner beams will only grow. Trust, born from verifiable experience and knowledge sharing, will continue to underpin the adoption of innovative techniques and materials in corner beam applications, thereby shaping the future skyline of cities worldwide.
Latest News
-
Brick Mesh Wall Solutions | Enhanced by GPT-4 Turbo Design
NewsAug.01,2025
-
Premium Anti-Climb Fence Spikes for Sale
NewsAug.01,2025
-
Premium Peach Post Fence | Durable & Stylish Security
NewsJul.31,2025
-
Best Galvanized Grating Price - Durable Galvanized Steel Grating Solutions
NewsJul.30,2025
-
0.5-4.0mm Wire 2×2 4×4 8×8 Hot Dipped Galvanized Welded Mesh Roll
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Metal Fence Pickets for Sale – Durable Galvanized & Steel Options
NewsJul.29,2025
Our company owns has excellent CAD steel grating drawing designers, who can provide customers with perfect steel grating layout design and better meet customers' special requirements for products. We have been adhering to it the business tenet of "quality first, customer first", with high-quality products, reasonable prices, and the fastest delivery time, we wholeheartedly provide customers with a full range of services! Welcome new and old customers to cooperate sincerely and create brilliance together!
Contact Us
WELCOME TO OUR COMPANY!
Thank you for your interest in our services! If you have any questions or wousld like to book a service, please don’t hesitate to contact us. Our team is dedicated to providing you with the highest level of service and support, and we are committed to working with you to make your event a success.
Service Email

Service Phone
Product Center
Contact Us
- Phone: +86 +86 15733154345
- E-mail: sales@chengsenchina.com
- Address: B1213 GLOBAL CENTER, NO.226 ZHONGHUA NORTH STREET, SHIJIAHUANG, CHINA