Grating
What Are the Different Types of Gratings Available, And How Do You Choose the Right One for Your Application?
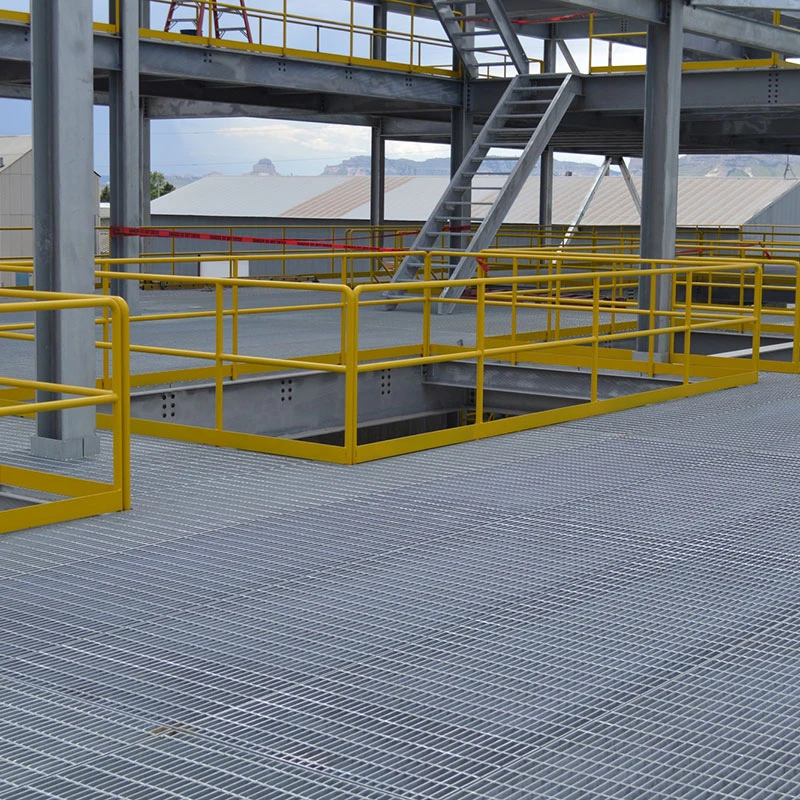
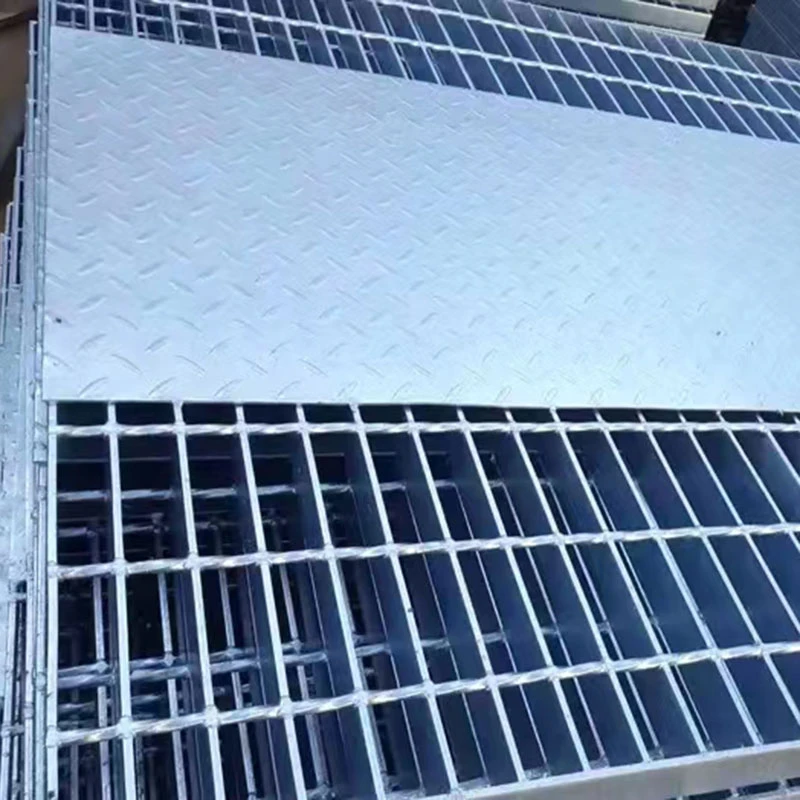
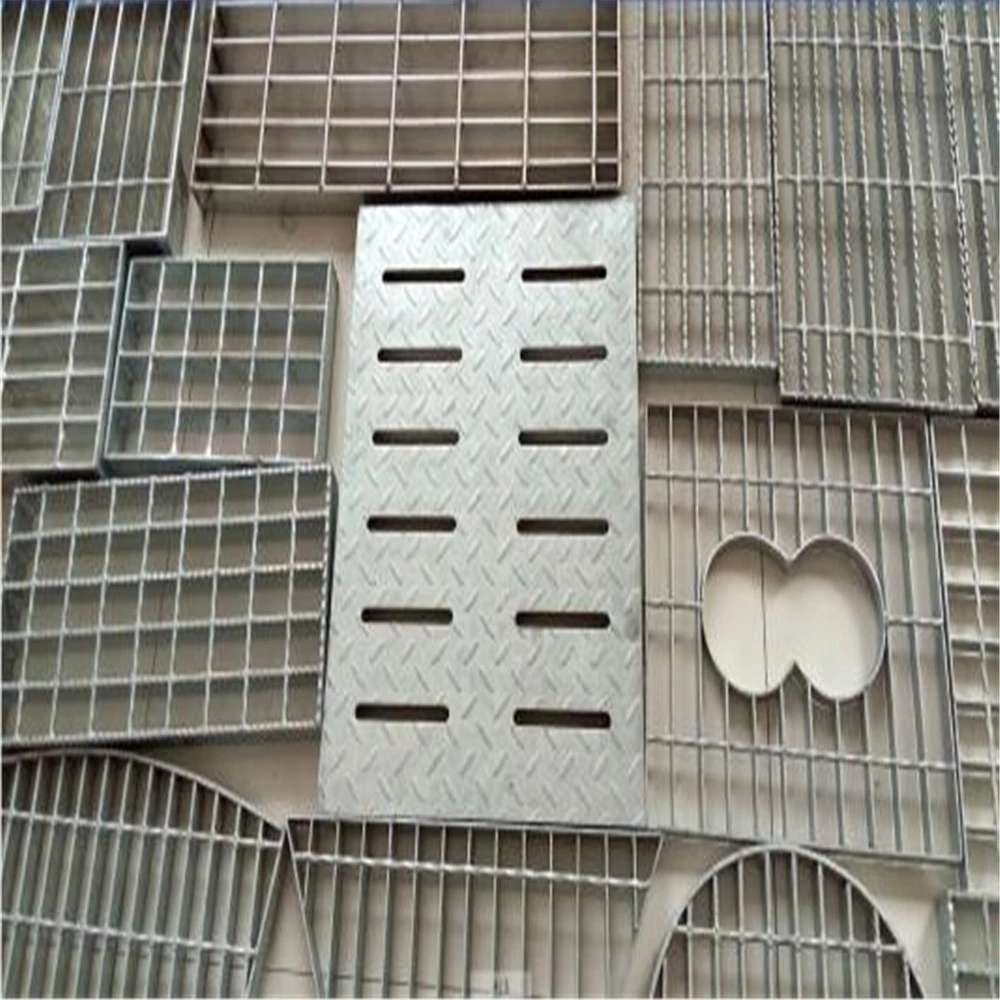
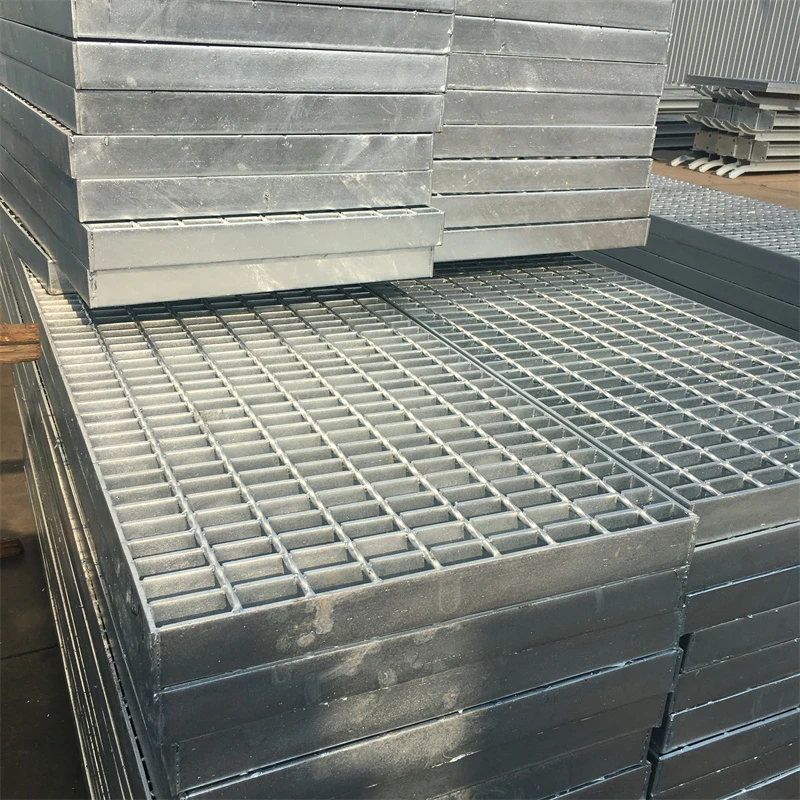
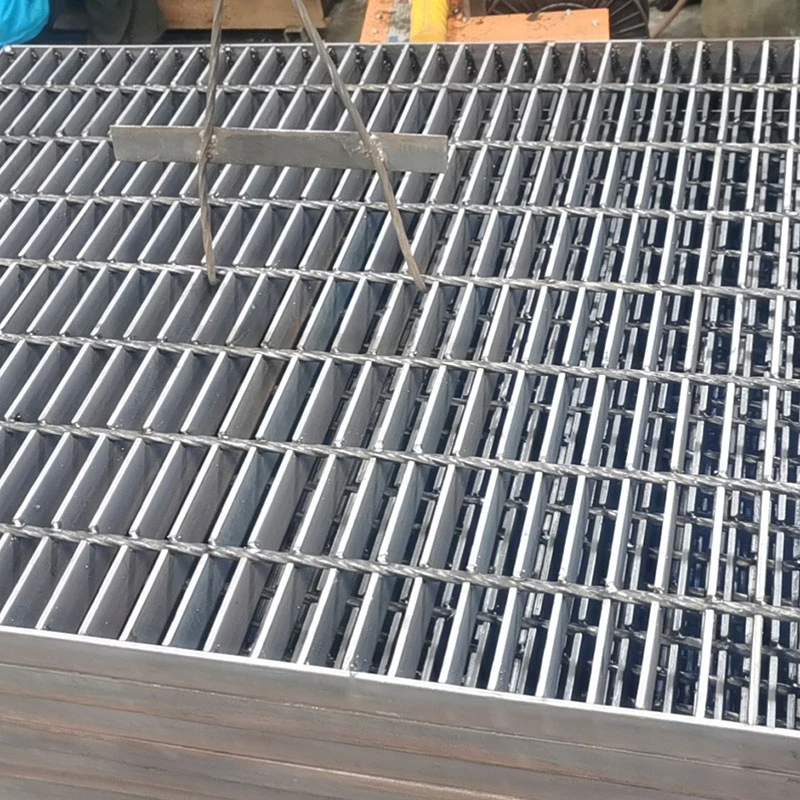
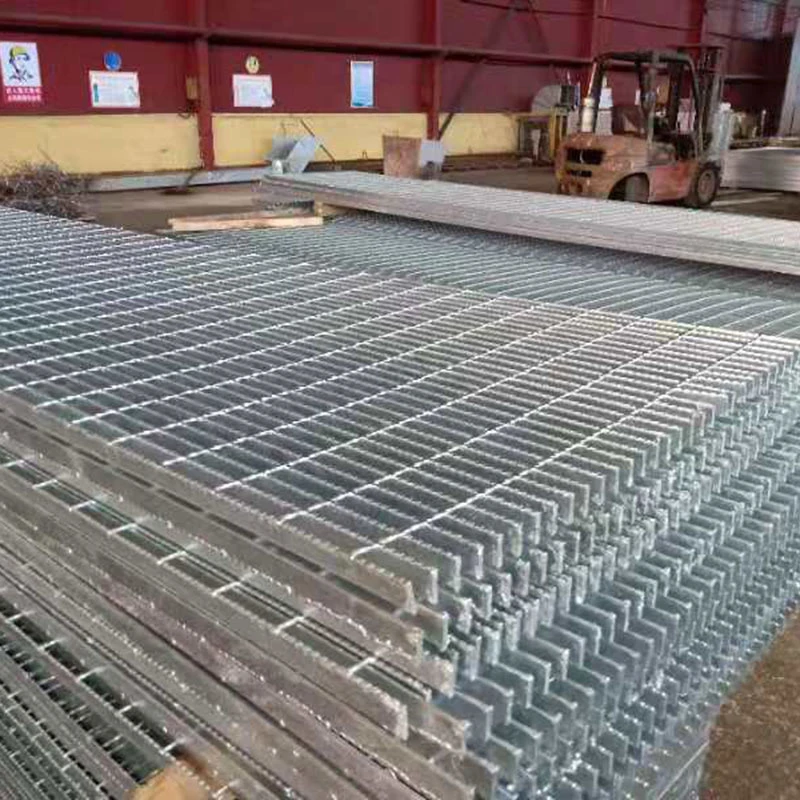
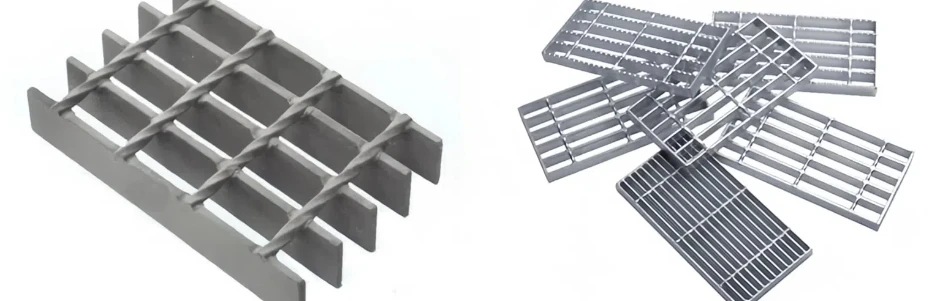
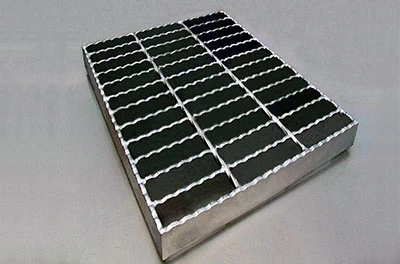
Gratings come in various types, each suited for specific applications depending on the material, design, and load requirements. The most common types of gratings include welded steel gratings, press-locked gratings, molded fiberglass gratings, and aluminum gratings. Welded steel gratings are made by welding horizontal bars to vertical cross bars, creating a robust and durable product ideal for heavy-duty industrial environments. These gratings are commonly used in areas such as walkways, platforms, and drainage covers where high load-bearing capacity is required. Press-locked gratings are produced by interlocking steel bars under high pressure, which eliminates the need for welding. They offer a slightly lighter design than welded steel gratings, making them suitable for less demanding applications. Molded fiberglass gratings are made by molding fiberglass resin into a grating pattern, offering excellent corrosion resistance and strength. These gratings are ideal for environments where exposure to chemicals, moisture, or extreme temperatures is common, such as in chemical plants, refineries, and coastal areas. Aluminum gratings, on the other hand, are lightweight, resistant to rust, and provide a smooth finish. They are often used in areas where aesthetic appeal is important or in environments where corrosion resistance is a priority, such as in marine or food processing industries. When choosing the right grating for a specific application, it’s important to consider factors such as the load-bearing capacity, environmental conditions, and the level of foot or vehicle traffic. For example, in areas with heavy machinery or high traffic, steel gratings may be the best choice, while fiberglass gratings are more suitable for chemical processing facilities. In addition, factors like slip resistance, ease of installation, and long-term maintenance should also be taken into account to ensure that the grating selected meets the specific needs of the application.
What Are the Benefits of Using Fiberglass Gratings, And Where Are They Commonly Used?
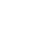
Iron, aluminum, stainless steel, and fiberglass gratings each offer unique benefits, making them suitable for various applications. Iron gratings are highly durable and have excellent load-bearing capacity, ideal for heavy-duty uses like industrial flooring and drainage systems. Aluminum gratings are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and easy to handle, making them perfect for marine environments, walkways, and architectural applications where weight reduction is critical. Stainless steel gratings provide a combination of strength, aesthetic appeal, and superior corrosion resistance, making them ideal for food processing facilities, chemical plants, and decorative designs requiring hygiene and durability. Fiberglass gratings, on the other hand, are non-conductive, lightweight, and resistant to chemicals and UV rays, offering low-maintenance solutions for harsh environments like wastewater treatment plants, offshore platforms, and slippery conditions due to their non-slip surface. Selecting the right material ensures optimal safety, performance, and cost-effectiveness tailored to the application’s demands.
What Are the Different Types of Gratings Available, And How Do You Choose the Right One for Your Application?
Gratings come in various types, each suited for specific applications depending on the material, design, and load requirements. The most common types of gratings include welded steel gratings, press-locked gratings, molded fiberglass gratings, and aluminum gratings. Welded steel gratings are made by welding horizontal bars to vertical cross bars, creating a robust and durable product ideal for heavy-duty industrial environments. These gratings are commonly used in areas such as walkways, platforms, and drainage covers where high load-bearing capacity is required. Press-locked gratings are produced by interlocking steel bars under high pressure, which eliminates the need for welding. They offer a slightly lighter design than welded steel gratings, making them suitable for less demanding applications. Molded fiberglass gratings are made by molding fiberglass resin into a grating pattern, offering excellent corrosion resistance and strength. These gratings are ideal for environments where exposure to chemicals, moisture, or extreme temperatures is common, such as in chemical plants, refineries, and coastal areas. Aluminum gratings, on the other hand, are lightweight, resistant to rust, and provide a smooth finish. They are often used in areas where aesthetic appeal is important or in environments where corrosion resistance is a priority, such as in marine or food processing industries. When choosing the right grating for a specific application, it’s important to consider factors such as the load-bearing capacity, environmental conditions, and the level of foot or vehicle traffic. For example, in areas with heavy machinery or high traffic, steel gratings may be the best choice, while fiberglass gratings are more suitable for chemical processing facilities. In addition, factors like slip resistance, ease of installation, and long-term maintenance should also be taken into account to ensure that the grating selected meets the specific needs of the application.
What Are the Benefits of Using Fiberglass Gratings, And Where Are They Commonly Used?
Iron, aluminum, stainless steel, and fiberglass gratings each offer unique benefits, making them suitable for various applications. Iron gratings are highly durable and have excellent load-bearing capacity, ideal for heavy-duty uses like industrial flooring and drainage systems. Aluminum gratings are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and easy to handle, making them perfect for marine environments, walkways, and architectural applications where weight reduction is critical. Stainless steel gratings provide a combination of strength, aesthetic appeal, and superior corrosion resistance, making them ideal for food processing facilities, chemical plants, and decorative designs requiring hygiene and durability. Fiberglass gratings, on the other hand, are non-conductive, lightweight, and resistant to chemicals and UV rays, offering low-maintenance solutions for harsh environments like wastewater treatment plants, offshore platforms, and slippery conditions due to their non-slip surface. Selecting the right material ensures optimal safety, performance, and cost-effectiveness tailored to the application’s demands.