Mar . 04, 2025 08:31 Back to list
type of brc mesh
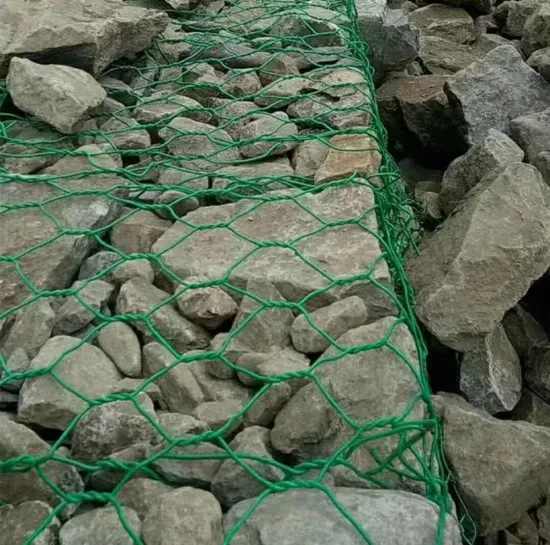
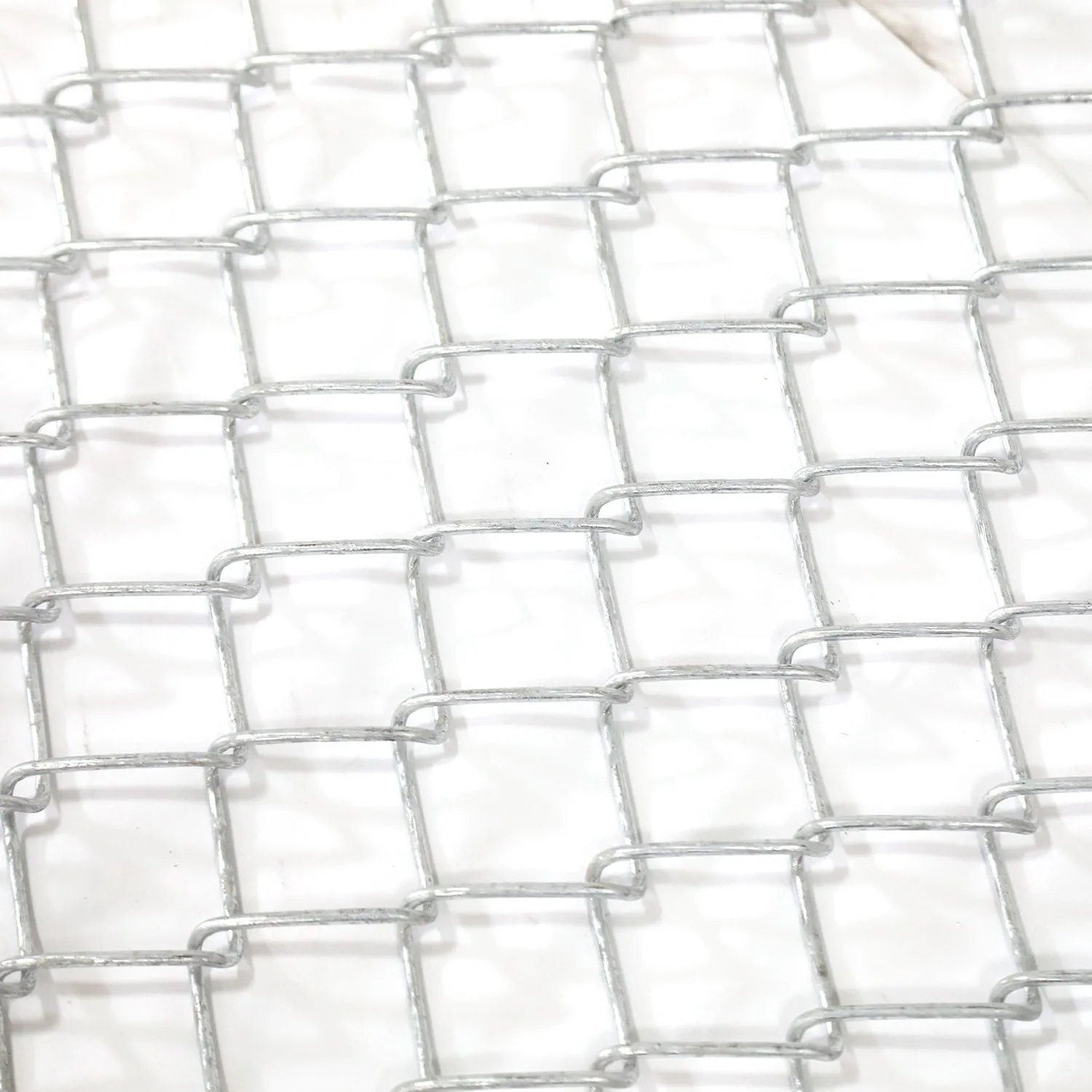

A critical insight for the discerning professional is the role of BRC mesh in sustainability and environmental responsibility within construction. Steel, the primary material in BRC mesh, is highly recyclable, aligning with the construction industry's shift towards sustainable practices. By opting for BRC mesh, contractors not only enhance structural integrity but also contribute to environmentally responsible building practices. Steel manufacturing and recycling processes have evolved over the years to reduce carbon footprints significantly, offering an ethical choice for construction companies aiming to improve their sustainability credentials. In practice, trustworthy suppliers and manufacturers become an invaluable asset for construction projects. Engaging with established suppliers ensures access to high-quality BRC mesh that complies with national and international standards. Professional relationships with reputable suppliers also facilitate effective logistical arrangements, ensuring timely delivery and support for project schedules. Contractors and engineers benefit from the reliability of trusted partners; this trust is essential in scaling projects efficiently and with minimal risk. For anyone involved in construction management or engineering, comprehending the authoritative role of BRC mesh extends beyond its immediate application. BRC mesh is not just a reinforcement product; it embodies decades of innovation in material science and construction technology. The sector continues to innovate, with current research exploring the integration of BRC mesh with advanced materials and smart technology for even more durable and resilient structures. In summary, the type of BRC mesh selected for a project should be informed by a comprehensive understanding of both the project’s demands and the mesh's properties. An expertise-driven approach considers wire gauge, mesh size, tensile strength, and environmental implications. Authoritatively selecting BRC mesh underpins the engineering success of concrete structures and signifies a commitment to sustainability, quality, and performance. For construction experts, the implementation of BRC mesh is not just a technique—it's a testament to industry leadership and an investment in the future of resilient and sustainable infrastructure.
Latest News
-
450mm Coil Diameter Galvanized Concertina Razor Wire - High Security
NewsAug.02,2025
-
Brick Mesh Wall Solutions | Enhanced by GPT-4 Turbo Design
NewsAug.01,2025
-
Premium Anti-Climb Fence Spikes for Sale
NewsAug.01,2025
-
Premium Peach Post Fence | Durable & Stylish Security
NewsJul.31,2025
-
Best Galvanized Grating Price - Durable Galvanized Steel Grating Solutions
NewsJul.30,2025
-
0.5-4.0mm Wire 2×2 4×4 8×8 Hot Dipped Galvanized Welded Mesh Roll
NewsJul.30,2025
Our company owns has excellent CAD steel grating drawing designers, who can provide customers with perfect steel grating layout design and better meet customers' special requirements for products. We have been adhering to it the business tenet of "quality first, customer first", with high-quality products, reasonable prices, and the fastest delivery time, we wholeheartedly provide customers with a full range of services! Welcome new and old customers to cooperate sincerely and create brilliance together!
Contact Us
WELCOME TO OUR COMPANY!
Thank you for your interest in our services! If you have any questions or wousld like to book a service, please don’t hesitate to contact us. Our team is dedicated to providing you with the highest level of service and support, and we are committed to working with you to make your event a success.
Service Email

Service Phone
Product Center
Contact Us
- Phone: +86 +86 15733154345
- E-mail: sales@chengsenchina.com
- Address: B1213 GLOBAL CENTER, NO.226 ZHONGHUA NORTH STREET, SHIJIAHUANG, CHINA