Jan . 25, 2025 02:58 Back to list
galvanized steel grating
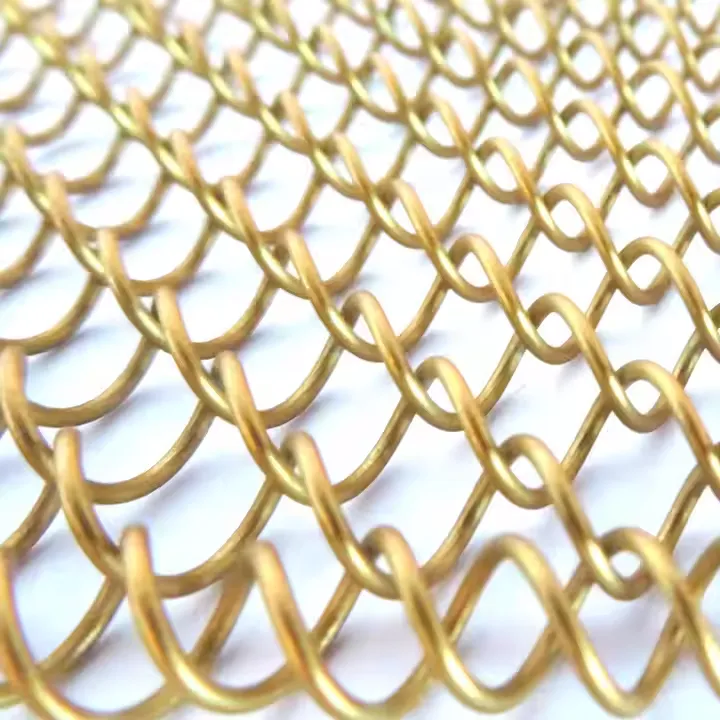

Moreover, professionals must pay heed to the finish of steel grating, which adds a layer of defense against wear and exposure. Galvanized finishes, achieved by submerging the steel in molten zinc, offer a formidable barrier against rust and enhance longevity, especially in outdoor placements. For environments that demand enhanced aesthetics alongside functionality, painted or powder-coated finishes allow customization that complements the surrounding architecture while providing additional protection. Practical experience in the field underscores the necessity for compliance with industry standards and regulations. Understanding and adhering to guidelines such as those provided by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) or the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) ensures that installations not only meet safety standards but also uphold quality benchmarks recognized globally. The emergence of advanced manufacturing techniques has further propelled the steel grating industry forward, spurring innovations such as serrated grating, which enhances slip resistance—a critical feature for safety-conscious industries. Serrated grating sees frequent use in oil rigs, chemical plants, and other industrial settings where worker safety is paramount. The advent of software-assisted design tools has equally empowered engineers to simulate grating performance under various stresses, leading to more informed decision-making processes in projects of all scales. In conclusion, the depth of expertise required to navigate steel grating details elevates the discipline to both an art and a science, demanding a comprehensive understanding of materials, engineering principles, and safety standards. Those in the industry, equipped with extensive knowledge and experience, play a crucial role in ensuring that steel grating not only fulfills its utilitarian purpose but also contributes aesthetically and safely to the infrastructure that supports our modern world. This confluence of expertise underscores the continued relevance and authority of steel grating in diverse applications across the globe.
Latest News
-
Brick Mesh Wall Solutions | Enhanced by GPT-4 Turbo Design
NewsAug.01,2025
-
Premium Anti-Climb Fence Spikes for Sale
NewsAug.01,2025
-
Premium Peach Post Fence | Durable & Stylish Security
NewsJul.31,2025
-
Best Galvanized Grating Price - Durable Galvanized Steel Grating Solutions
NewsJul.30,2025
-
0.5-4.0mm Wire 2×2 4×4 8×8 Hot Dipped Galvanized Welded Mesh Roll
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Metal Fence Pickets for Sale – Durable Galvanized & Steel Options
NewsJul.29,2025
Our company owns has excellent CAD steel grating drawing designers, who can provide customers with perfect steel grating layout design and better meet customers' special requirements for products. We have been adhering to it the business tenet of "quality first, customer first", with high-quality products, reasonable prices, and the fastest delivery time, we wholeheartedly provide customers with a full range of services! Welcome new and old customers to cooperate sincerely and create brilliance together!
Contact Us
WELCOME TO OUR COMPANY!
Thank you for your interest in our services! If you have any questions or wousld like to book a service, please don’t hesitate to contact us. Our team is dedicated to providing you with the highest level of service and support, and we are committed to working with you to make your event a success.
Service Email

Service Phone
Product Center
Contact Us
- Phone: +86 +86 15733154345
- E-mail: sales@chengsenchina.com
- Address: B1213 GLOBAL CENTER, NO.226 ZHONGHUA NORTH STREET, SHIJIAHUANG, CHINA