Jan . 10, 2025 12:42 Back to list
different types of drywall corner bead

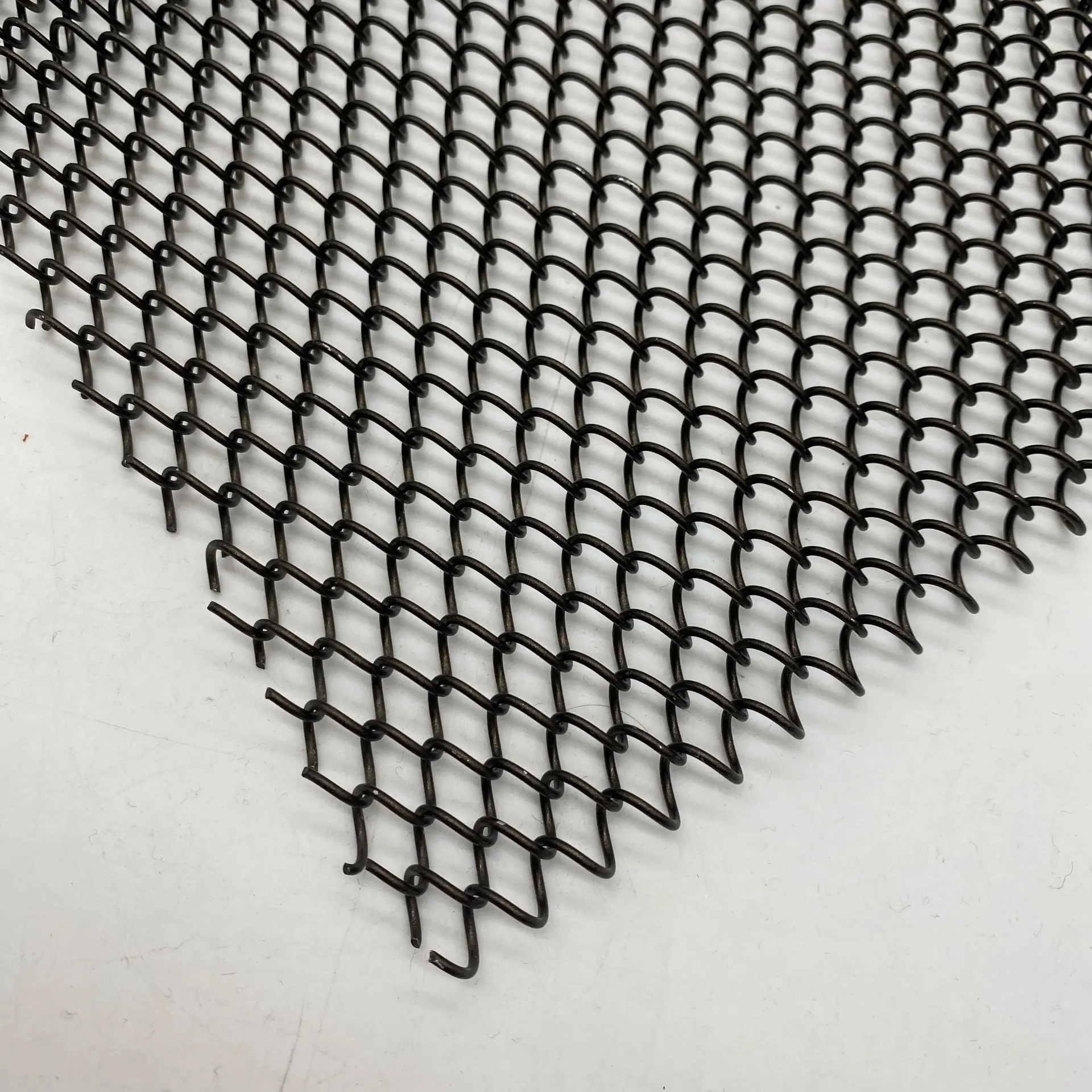
One must not overlook echelle gratings, recognized for their high dispersion and blazing efficiency in high-order diffraction scenarios. Echelle gratings are integral to high-resolution spectrometers due to their ability to handle multiple wavelengths simultaneously, making them a staple in astronomical and atmospheric studies. Their durability and efficiency make them a trusted component in environments where precision cannot be compromised. Reflective gratings, often synonymous with mirrors in functionality, focus light through reflection rather than transmission. This makes them particularly useful in laser applications, where maintaining beam integrity and minimizing loss is critical. The expertise in engineering reflective gratings lies in optimizing the coating materials and groove profiles to meet specific reflective indices and efficiency standards. In more specialized uses, transmission gratings, which diffract light through passages in a transparent substrate, highlight advancements in fiber optics and holographic projections. Their construction requires meticulous attention to the refractive indices and thickness of the substrate, areas demanding specialized knowledge and experience. Exploring the diverse world of gratings involves an appreciation of both their intricate construction and varied applications, which collectively enhance their authority in the optical industry. By understanding these different types, professionals can select the appropriate grating type that aligns with their application-specific needs, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency. Trust in these technologies continues to grow as advancements are made, driven by the accumulating expertise and experience of engineers and scientists in the field.
Latest News
-
Brick Mesh Wall Solutions | Enhanced by GPT-4 Turbo Design
NewsAug.01,2025
-
Premium Anti-Climb Fence Spikes for Sale
NewsAug.01,2025
-
Premium Peach Post Fence | Durable & Stylish Security
NewsJul.31,2025
-
Best Galvanized Grating Price - Durable Galvanized Steel Grating Solutions
NewsJul.30,2025
-
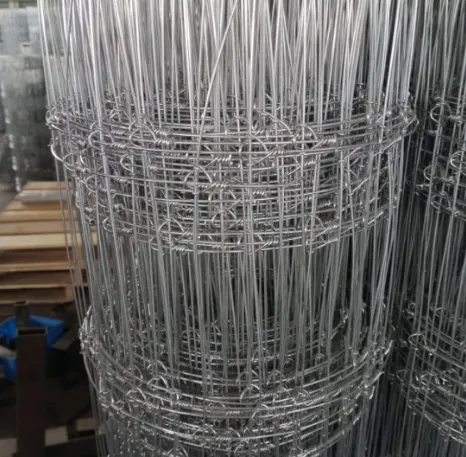
0.5-4.0mm Wire 2×2 4×4 8×8 Hot Dipped Galvanized Welded Mesh Roll
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Metal Fence Pickets for Sale – Durable Galvanized & Steel Options
NewsJul.29,2025
Our company owns has excellent CAD steel grating drawing designers, who can provide customers with perfect steel grating layout design and better meet customers' special requirements for products. We have been adhering to it the business tenet of "quality first, customer first", with high-quality products, reasonable prices, and the fastest delivery time, we wholeheartedly provide customers with a full range of services! Welcome new and old customers to cooperate sincerely and create brilliance together!
Contact Us
WELCOME TO OUR COMPANY!
Thank you for your interest in our services! If you have any questions or wousld like to book a service, please don’t hesitate to contact us. Our team is dedicated to providing you with the highest level of service and support, and we are committed to working with you to make your event a success.
Service Email

Service Phone
Product Center
Contact Us
- Phone: +86 +86 15733154345
- E-mail: sales@chengsenchina.com
- Address: B1213 GLOBAL CENTER, NO.226 ZHONGHUA NORTH STREET, SHIJIAHUANG, CHINA